Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) are a subset of machine learning and form the base for deep learning. The name is inspired by the complex network of neurons that exist in the human brain.
Neural networks are a set of algorithms that mimic the operations of a human brain to recognize relationships between vast amounts of data and produce logical outputs as we do.
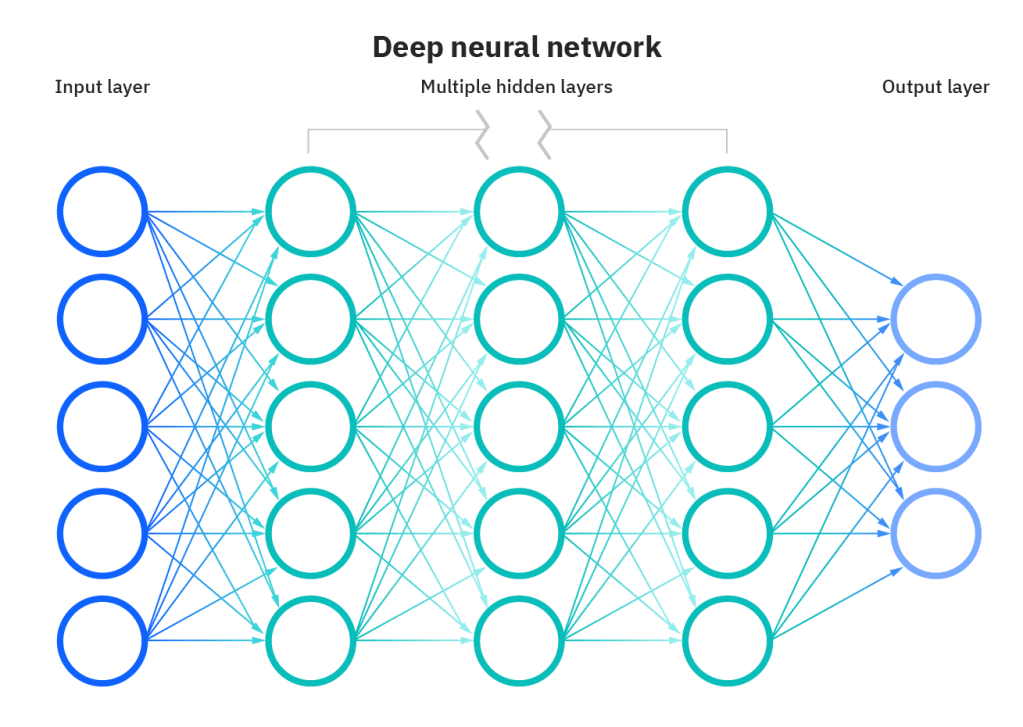
ANNs comprise of node layers, that contain one input layer, one or more hidden layers, and one output layer. Each node connects to another (in another layer) and has an associated weight and threshold.
In the human brain, the neurons are activated for some data inputs. These activated neurons pass information to the next layer and eventually, an output is generated. No information is passed otherwise. In ANNs however, a neuron (node) only gets activated if its output is above the threshold value.
Once trained, ANNs are very powerful tools and can be used for speech recognition, image recognition, self-driving devices, etc.

How do they work?
Let’s think of each individual node as its own linear regression model, composed of input data, weights, a bias (or threshold), and an output. The formula would look something like this:

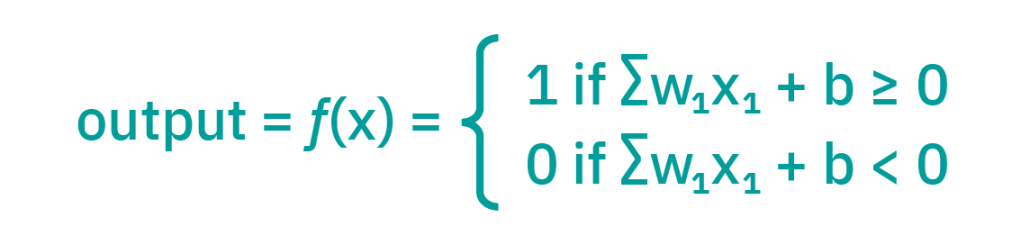
Once an input layer is determined, weights are assigned. These weights help determine the importance of any given variable, with larger ones contributing more significantly to the output. All inputs are then multiplied by their respective weights and then summed.
Afterward, the output is passed through an activation function, which determines the output. If that output exceeds a given threshold, it activates the node, passing data to the next layer in the network. This results in the output of one node becoming the input of the next node. This process of passing data from one layer to the next layer defines this neural network as a feedforward network.
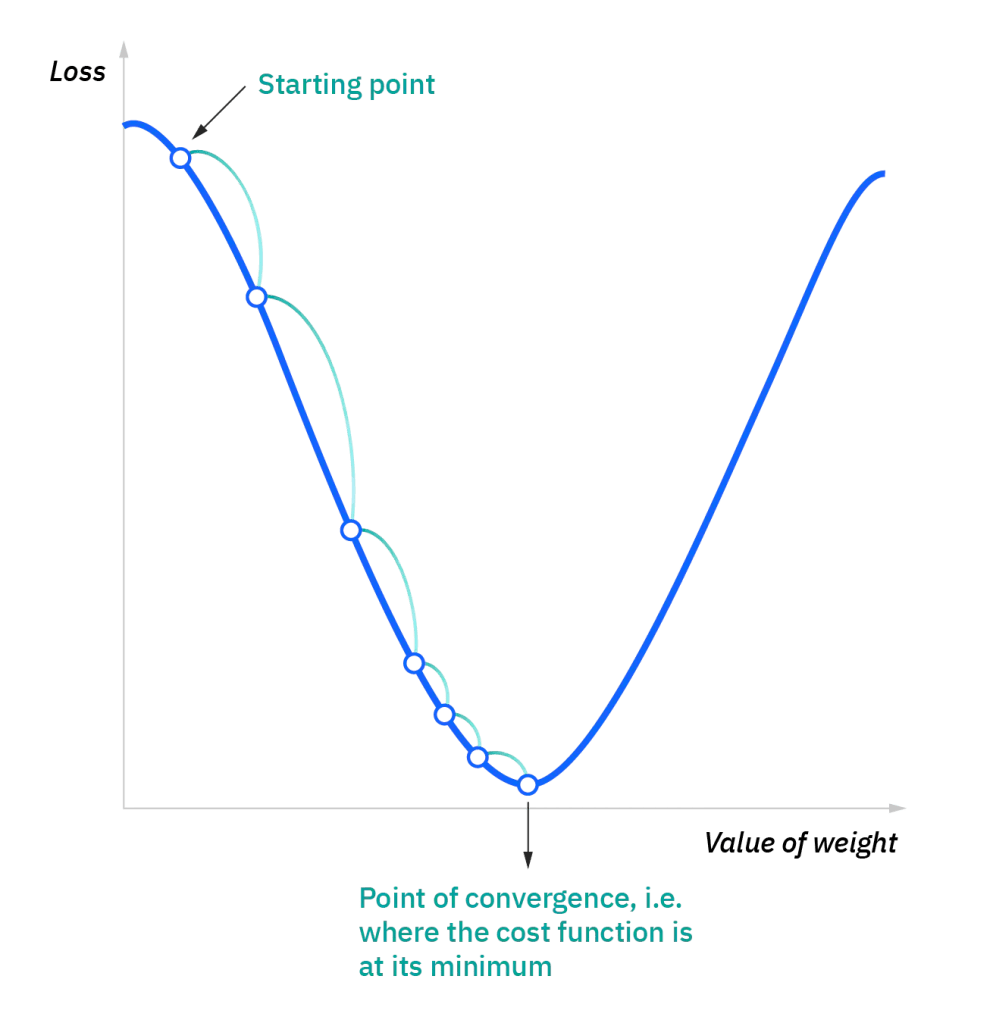
Once the training is finished, we can measure the performance using a loss/ cost function like Mean Squared Error. The ultimate goal would be to reduce the cost function to ensure better performance and reduce errors. This is done using gradient descent.
Article reference
Leave a comment